New Equilibrium Biosciences has developed a computational–experimental platform to discover lead drug candidates that regulate intrinsically disordered proteins implicated in cancers and neurodegenerative disorders.
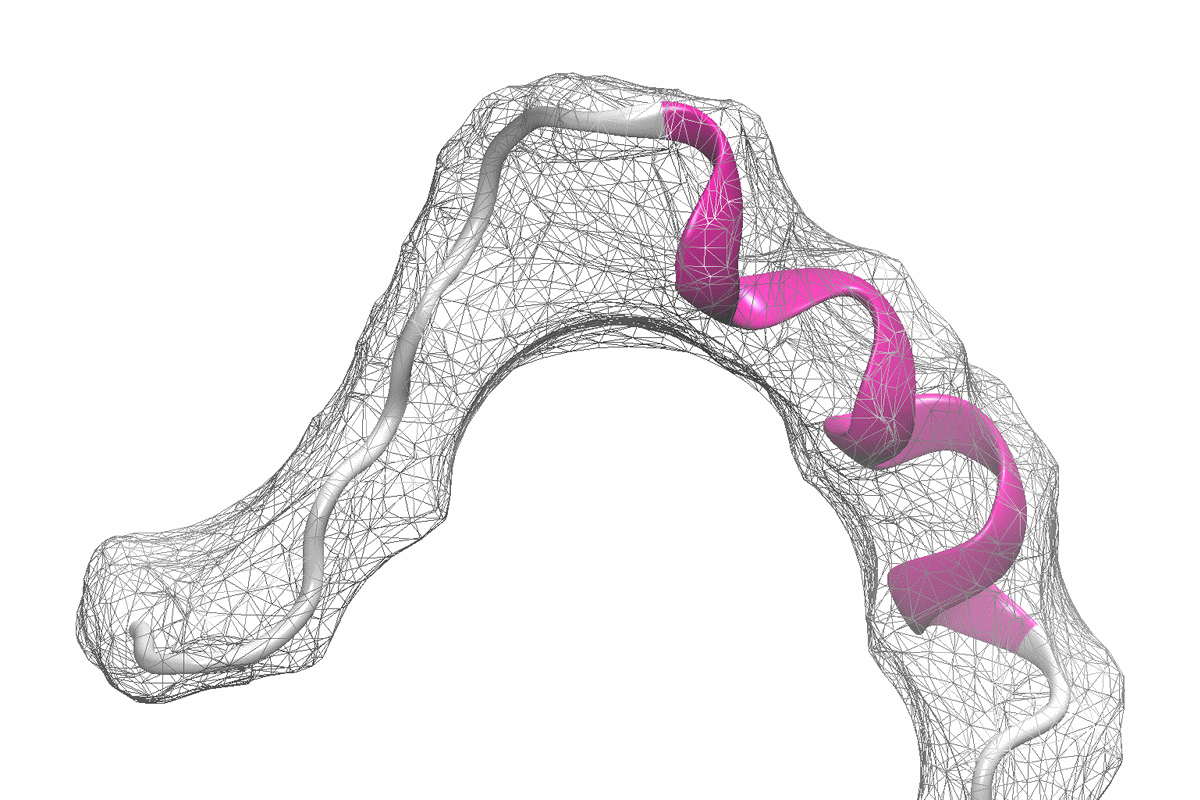
The company says that about 30% of proteins are predicted to not have a single 3D structure. Instead, they have evolved to fluctuate between an ensemble of short-lived conformations, which enable them to perform essential functions in cells. Many proteins implicated in cancers and neurodegenerative disorders, as well as many bacterial and viral proteins, belong to this class of shapeshifting proteins, termed intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs). For these proteins, obtaining detailed structural information that can guide structure-based drug discovery is challenging, making it very difficult to target these proteins.
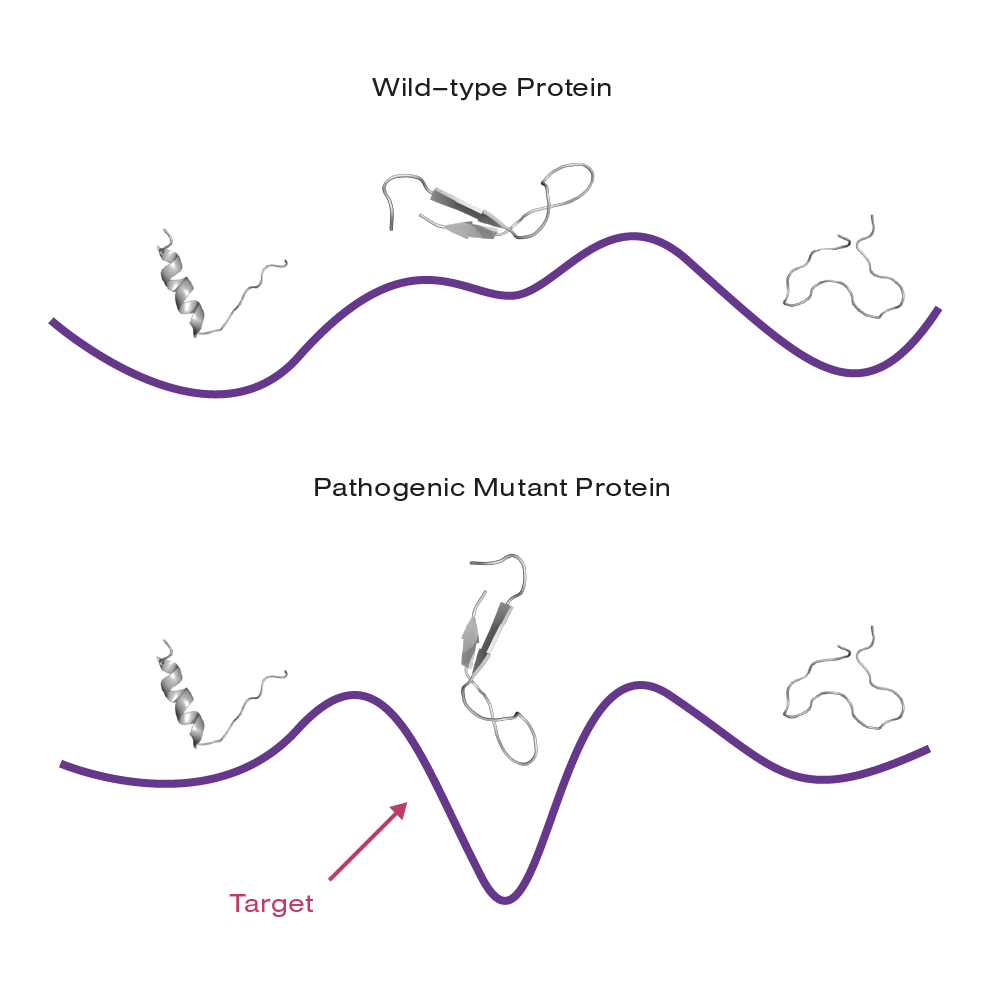
By solely targeting pathogenic conformations in diseased cells, the healthy protein remains unimpaired, presenting a new route to low-toxicity drugs.
Existing technologies, developed to describe compact and stable proteins, have not been able to consistently capture the extended conformations adopted by IDPs or the timescales at which they fluctuate.
New Equilibrium combines big data, artificial intelligence, and biophysical experiments to freeze-frame IDPs, allowing it to accurately visualize the ensemble of different conformations that an IDP adopts. This 3D structural information enables New Equilibrium to design and optimize drugs targeting IDPs using structure-based drug design methods.
The strategy is to specifically drug malfunctioning IDPs and restore normal cellular function. First, the company utilizes bioinformatics and mutagenesis assays to identify the functional roles of individual IDP states. Next, they compare the set of conformations adopted by a “wild-type” protein in healthy cells and those from an impaired form of the protein in diseased cells. By solely targeting pathogenic conformations in diseased cells, the healthy protein remains unimpaired, presenting a new route to low-toxicity drugs.
Target IDPs include p53 (Tumor suppressor with mutations in over half of tumors); Amyloid BETA (Normally disordered, but forms aggregates in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients); and ccda (Bacterial antitoxin protein that releases a toxin to trigger cell death).
Founded in 2019, New Equilibrium is part of the Petri accelerator and has received an NSF SBIR Phase I Award that started in September 2020.
